Medical Device Design Considerations
NOTE: This article/blog is Copyright TronicsZone. It cannot be reproduced without prior written approval.
Introduction
Electronic devices are indispensable in medical procedures. Starting from diagnosis to treatment almost all the steps in medication involve one or another electronic device. The recent inspiring advancement in medical electronic device is the robotic surgery equipment that assists doctors to perform surgeries from remote places.
Even the classic mercury-based thermometers are being replaced with IR based thermometers pertaining to their ease of use and non-contact mode of operation. The main concerns in medical product design are safety, compliance, and reliability.
This article discusses in brief on design considerations, registration policies and compliance protocols followed during medical device design from the perspective of Electronic Product Design in particular.
Importance of Medical Device Design
Electronic equipment in the medical arena is widely used for diagnosis and treatment of spontaneous illness and physiological disorders. Sensors play an important role in such devices. Sensing elements capable of monitoring temperature, pressure, airflow, blood-flow are the most sought-after sensors.
These devices reduce the time taken for diagnosis and thus aid the doctors to make informed decisions quickly. In fact, these devices have brought a revolution in the mode and quality of treatment provided. Some of the most important applications where medical electronic devices are used are listed below.
- Blood analyzer – Blood vitals checking, Antibody identification, Glucose level monitoring
- Blood Pressure analysis – Hypertension analysis
- Monitoring Pulmonary functions – Airflow monitors
- Imaging in Diagnostics – MRI – Magnetic resonance imaging
- Ultrasound scan – Pregnancy diagnosis and treatment
- Temperature monitors
Steps and Considerations in Product Design
Medical application is a critical area where high precision, safety, and reliability are the key factors. The design steps and the factors to be considered in medical device design are
Identification and Design team classification
Identification involves in assessing the market requirement to decide on the components and the technology required. A strong product definition improves the product design cycle speed. The second step is to classify the design teams for product design. Medical electronic product design is a complex challenge and requires multidisciplinary inputs. The design teams typically comprise of
- Engineering and design resources
- Resource with Clinical and Scientific Knowledge in Medical industry
- Intellectual property related documentation team
- Regulation, compliance certification and quality assurance team
Precision
Precision and accuracy are the most important factor affecting the quality of a medical device. A good treatment depends on an accurate diagnosis. Proper analysis prior to design must be made to maintain precision throughout the lifetime of the device.
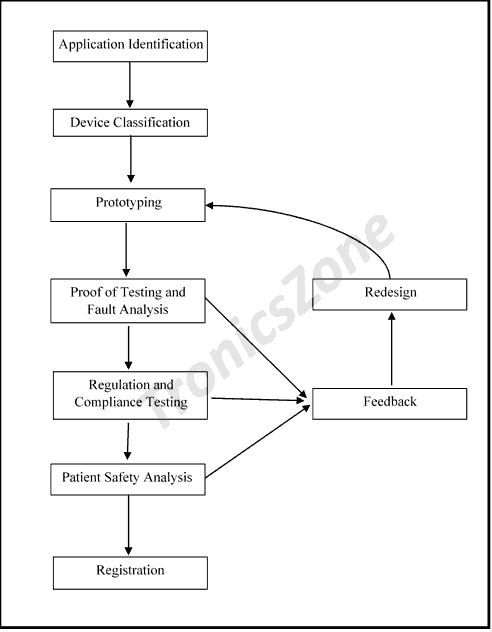
Lifetime and Redundancy checks
Lifetime of a medial device is critical to ensure quality and longevity. During design and testing the device, methods like single point of failure analysis, failure mode and effect analysis are performed to improve the reliability. The idea of improving the device life lies in proper maintenance and quick servicing.
Redundancy checks are also be performed on the device in periodic intervals. Due to frequent changes in government regulation and improvement in technology some device or a part of the device may become redundant. In this case, specific alterations are performed to validate the device. Redundancy check is to ensure that the device design is up to date.
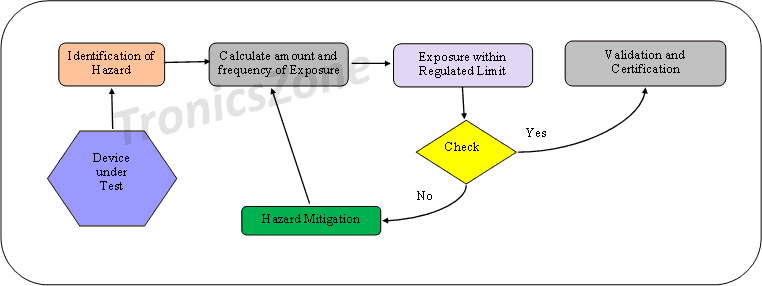
Patient Safety analysis
Patient safety is the most prominent factor to be considered during medical device design. Safety analysis shall be performed both before and after design. Prior to the physical design of the device, hazard identification and mitigation are done. This improves the safety provisions in the design. The flowchart is as given below.
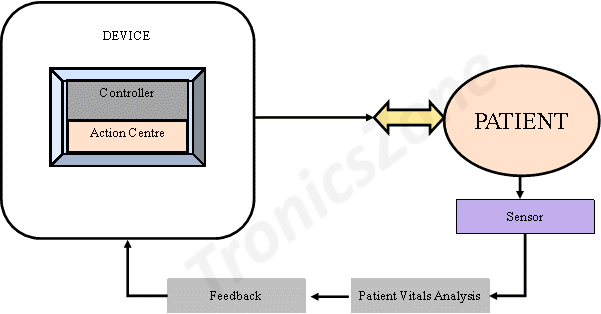
After the design is complete onsite safety to patients shall be ensured through a dedicated feedback system. The safety system comprises a controller, a feedback sensor and an action centre. This system relies on sensor feedback data collected from the patient to either scale up or scale down the device output. This on-board safety systems are essential in case of intrusive surgical equipment such as laparoscopic surgical devices where there is direct contact between the patient and the device.
Fault Analysis for Device Validation
Designers begin fault analysis on a device with a functional diagram of the device. Fault analysis is usually done on the prototype of the device. Fault may arise due to mistakes in fabrication, component malfunctioning, current of voltage spikes. Mitigating and redesigning after fault analysis is done to improve the performance of the device.
Single Point of Failure Analysis
Single point of failure is the failure in any part/component of the device such that renders the whole system ineffective. For example, in a digital sphygmomanometer device, the blood pressure sensor is the most prioritized component. Any issue with this will make the complete device useless. Hence single point of failure test is done to ensure the reliability and the longevity of the blood pressure sensor.
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FEMA)
FEMA is a review tool to validate a design and it is used to identify and correct all possible failures in a product, or a manufacturing process. Failure mode stands for the ways, or modes, in which the device may fail to meet the requirements. Failures may be due to any errors, defects or even improper usage. The consequent effect of the failure on the device performance is measured.
- First the system is broken down in smaller functional blocks
- Review block by block and analyze all the possible ways it could fail
- Analyze the effects and find risk criteria
- Lastly device a plan to mitigate the failures
FEMA is an iterative process aimed at improving the quality and reliability of a product.
Bio-Compatibility testing
Medical devices that are supposed to have physical contact with the patient are subjected to Bio-Compatibility testing. Categories such as cytotoxicity, sensitivity, and irritation are tested to provide Bio-Compatibility certificate. Based on the time of total contact the categories are
- Case “I” – limited (<= 24 hours),
- Case “II” – prolonged (> 24 hours to <= 30 days), and
- Case “II” – permanent (> 30 days).
ISO 10993-1 certificate is essential to design Bio-Compatible devices. Carcinogenic tests are also taken to study the effects of prolonged exposure.
National Medical Device Policy
In India, the latest medical device policy was announced in 2017. The policy is aimed to assist the government in programs like free diagnostics, free secondary level care, National Dialysis Program, and National Health Assurance Program. The Indian government has instituted the National Medical Devices Promotion Council in January 2020 to promote the Medical Device Industry (MDI) sector and promote Make in India Scheme. The steps for device registration and certification are as follows.
Registration
Registration of MDI manufactures and their regulation in India is centrally done through the Central Drug Standards Control Organization (CDSCO). CDSCO has both Central Licensing Authority (CLA) and State Licensing Authority (SLA) to provide licences to Import, Manufacture for sale or for distribution and sale. The list of regulated products is released by CDSCO. To register with CDSCO
- Determine whether the products to be designed fall under regulated category
- Prepare necessary documents and upload registration
- Furnish required certificates
Non-regulated medical devices are approved by the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI). All approvals are subjected to case by case analysis and sometimes clinical testing. Indian indigenous Quality Council of India (QCI) provides two certificates the ISO 9001 based ICMED 9000 certificate and the ISO 13485 based ICMED 13485 certificate. ICMED is the abbreviation for the Indian Certification of Medical Devices Scheme.
Audit and Certification
In India, form MD-14 is used to file device compliance application. This includes manufacturing facility information, device technical information, testing results, and clinical data.
ISO 13485:2016 (Medical devices – Quality management systems – Requirements for regulatory purposes) is the certificate required to file compliance to Indian standards. Audit and certification in South Asia including India is provided by private concerns like TÜV SÜD, TÜV Rheinland, etc., IEC 60601-1 is followed for Electrical Medical Equipment such as ECG machines.
International Compliance Protocols
For Export of medical devices, it is necessary to meet the international compliance standards. Given below is a compilation of international compliance standards.
- IEC 60601-1: Medical electrical equipment
- IEC 61010-1: Electrical equipment safety requirements for measurement and use in a laboratory
- IPC 6011: Printed Circuit Boards
- ISO 13485 Medical Devices: Quality Management System
- US FDA 21 CFR Part 807: Manufacturer regulation in USA
- ISO 14971 Medical Devices: Risk Management in Medical Devices
Conclusion
Medical devices are a critical and lifesaving tools. Utmost care is required to ensure that design meets all the safety and compliance requirements. Functional design followed by prototyping the product and testing the prototype for functionality and safety are the key steps involved in device design which are duly followed at TronicsZone.
Fault analysis such as single point of failure tests, failure mode and effect analysis tests come in handy to foresee the faults and design the device robustly and ensure reliability. ISO 13485 is the basic standard to be followed to obtain compliance of medical devices in India or abroad.
Patient safety, compliance, precision, and reliability are thus the key for medical device design.
NOTE: This article/blog is Copyright TronicsZone. It cannot be reproduced without prior written approval.

 TronicsZone
TronicsZone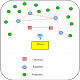 TronicsZone
TronicsZone