IoT Mesh Network – Things you need to know
NOTE: This article/blog is Copyright TronicsZone. It cannot be reproduced without prior written approval.
Introduction
Internet of Things (IoT) technology relies on reliable networking to operate desirably. Wireless communication is preferred over wired communication owing to scalability and ease of operation. When it comes to wireless communication in IoT, technologies such as Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Bluetooth shall be utilized to establish a network.
Since IoT is a highly customized application, one size does not fit all. So, care must be taken while selecting the type of network. This article analyses on the use of a IoT Mesh Network in an IoT hardware setup, and its pros and application areas.
Wireless Mesh Network in an IoT application
A mesh network or a mesh topology depends on excessive interconnectivity. All the nodes have at least two ways/paths to transmit and receive data. Every node in mesh topology relates to other multiple nodes and they communicate among themselves and the router or gateway.
Establishing a perfect mesh in a wired scenario can be complicated, but in a wireless scenario, with the advent of low-power communication protocols, it is comparatively easier to establish mesh topology. The main advantages in choosing mesh network in an IoT application are
Scalability
IoT relies on customization and adaptability. Mesh network ensures the addition of new nodes or sensors very easily. Removal of nodes is also equally simple. When nodes are added in a mesh network, more paths are established and unlike in other topologies, the communication speed and the reliability improve.
Self-Configuring
Mesh networks are self-configuring as have auto-discovery capabilities. New nodes can be calibrated and connected to the internet without much effort. Previous setup is not required. This allows the designer to expand and administrate the network easily.
Self-Healing
A mesh network can recover from a communication failure by itself. External intervention required is minimal. As the nodes in a mesh are always in constant discovery process, the nodes always find the best possible path to reroute data in case of failure. Algorithms, like Shortest Path Bridging, make sure that nodes that are active alone are used for communication.
Reliability and cost benefit
These advantages make the mesh network faster, reliable, and error-free. Moreover, the cost of maintaining a mesh network is low compared to other topologies as it requires minimal manual intervention. Low-power sensors, nodes are available for mesh networks.
All these make the mesh network, a reliable network topology to be used in an IoT application.
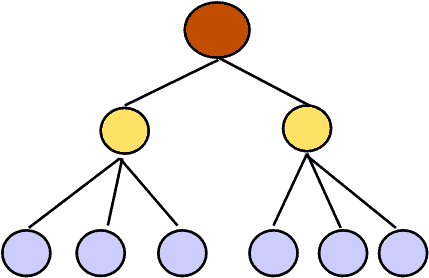
Partial Mesh Network
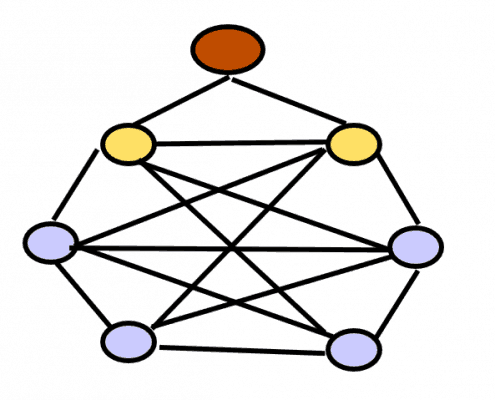
Full Mesh Network
IoT Mesh Network & its main components
A standard mesh network consists of three components. They are Gateways, repeaters and Endpoints/End-nodes.
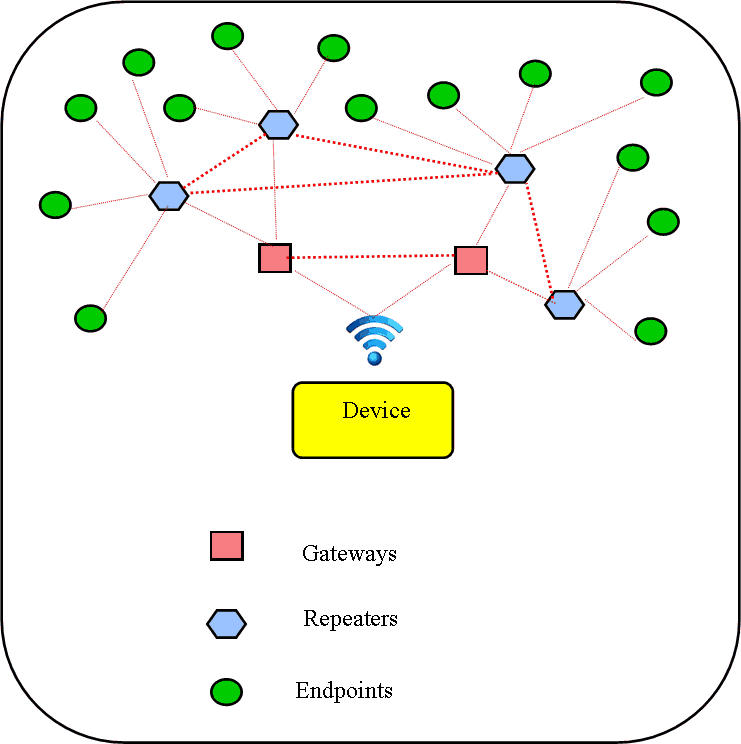
Gateways
Gateways are usually routers with modem that have a connection with the internet. Gateways establish communication with all the nodes and to the central controller/server through the internet. They serve as the backhaul between the internet and the local mesh IoT network. Gateways also have higher security and selection algorithms than repeaters and the nodes.
Repeaters
Repeaters are routers basically performs signal replication and transmission. They are designed to forward and receive messages between end devices (endpoints) and the gateway in a mesh network. The repeaters are designed not to go into sleep mode, that is they are always left in the active state to enable proper performance of the mesh network.
Endpoints/Nodes
In an IoT setup, the endpoints or the nodes are usually a sensor. They collect and transmit data to the server through router and gateway via the internet. They do not have routing capability and can get into sleep mode when not in use. This ensures power reduction.
Mesh Network Communication Protocols
In a mesh network, a data packet in the network hops from node to another till it reaches the intended node or passes out through an intended internet gateway. Therefore, it is necessary to have a connection between every node to make the communication path simple or latency will increase as the data has to jump between nodes through a central network back and forth.
Wireless communication protocols such as Wi-Fi, Zigbee, Z-Wave, Bluetooth are preferred in mesh construction. The benefits of all these protocols are discussed below.
Wifi Mesh Network
Traditionally, Wifi has been a star network with the devices communication with a single Wifi router. However, recently several Wifi router manufacturers have started implementing Wifi mesh network support in their routers so that the routers form a mesh network amongst themselves & the devices can seamlessly connect between any of the routers forming the mesh network.
ZigBee
Zigbee comes under IEEE 802.15.4 for low-rate wireless personal area networks. The latest protocols Zigbee pro and Zigbee 3.0 are operating across 2.4 GHz and sub-GHz—868 MHz and 915 MHz—bands are very low cost and low power applications. Zigbee based mesh network are best suitable for applications such as security systems, industrial automation, environmental control sensors, and medical applications.
Thread Protocol
Thread is also based on IEEE 802.15.4. typically designed for IoT mesh communication, thread offers better integrity than Zigbee in interoperability, architecture, and security. Thread is specially designed for home automation wireless communication. This is a low-power, battery-operated wireless mesh networking protocol, based on IPv4 and IPv6.
Thread allows devices to talk to other IoT nodes and directly to the server through the cloud. They have better self-healing and self-configuring capabilities. Zigbee requires a gateway with a modem to convert data into IP packets, while Thread requires only a border gateway as it already works on an IP-based protocol.
Lightweight Mesh (LWMesh)
LW Mesh is another IoT mesh protocol based on IEEE 802.15.4. This protocol is designed for domestic and industrial automation.
Bluetooth Mesh Network
BLE is the Bluetooth Low Energy protocol operating frequencies in the range of 2402–2480 MHz. BLE is compatible with a network that requires small coverage distance and requires low-power and low-cost networks composed of many nodes. One of the major advantages of BLE is interoperability with most current devices such as laptops, smartphones, and mobile tablets.
BLE is garnering great attention especially in industrial scenarios where many nodes are placed close to each other. Some issues pertaining to security are still open in BLE for a mesh application. Moreover, Bluetooth/BLE provides only partial connectivity as a gateway modem is required to connect this network with the cloud to send and receive data over the internet.
Z-Wave
Z-Wave is a sub-1 GHz wireless mesh network protocol smart home product, such as lights, security systems and door locks. This protocol focused on simple command and control and may not fit in with complex algorithms. Z-wave provides better interoperability and backward compatibility.
For a small network Thread, Zigbee and Bluetooth mesh provide similar performance. At higher payloads Thread and Zigbee outperform Bluetooth. Bluetooth mesh is best is the payload is smaller. With an increase in the size of the network, all the protocols have an increase in latency. This can be reduced by choosing better routing algorithms.
Applications areas of Mesh Network in IoT
Mesh networks in IoT applications are essential in areas where many IoT sensors are used, and high accuracy is expected. Smart City projects have large data sourced from traffic signals, public places etc. Such an application will be benefited using Mesh topology.
Medical applications with mesh IoT networks ensure 24×7 monitoring of the patients. Smart home automation, industrial process automation, and irrigation automation are some areas that require mesh networks.
The critical shortcoming in the mesh network are latency and utilization ratio when the network is small and used less frequently. But the advantages of mesh outweigh the drawbacks. Home automation projects are better suited with Z-wave and Thread protocols.
Industrial applications can be handled using BLE and Zigbee protocols. BLE can be slightly power consuming than Zigbee. Depending on the type of application the mesh network and the technology shall be selected.
We at TronicsZone have hands on-experience in this area. For further information on types of communication protocols used in IoT, refer to Communication Protocols in IoT Devices
NOTE: This article/blog is Copyright TronicsZone. It cannot be reproduced without prior written approval.


 TronicsZone
TronicsZone